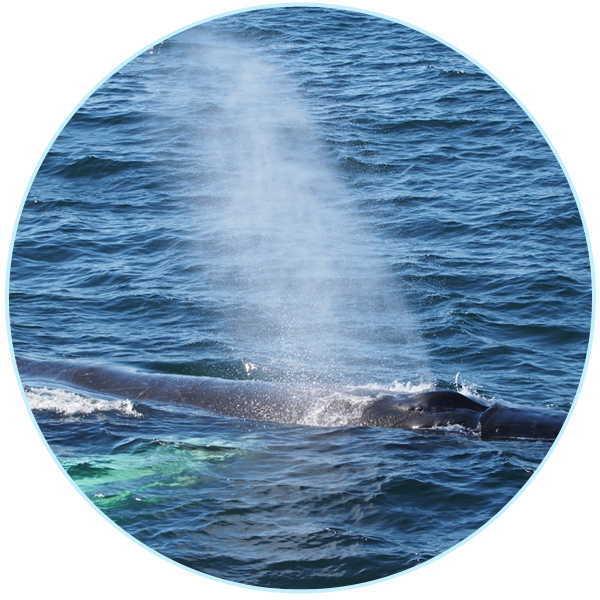
This past weekend, 19 undergraduate students from the University of Maine and Dr. Kristina Cammen traveled aboard the Schoodic Ferry from Bar Harbor to Winter Harbor to check out the Schoodic Center whale museum. On the way, (amidst the fog) they spotted harbor porpoise and gray seal, several sea birds, and interesting upwelling patterns. The students also had the opportunity to talk with a professional marine mammal observer, and learn about internship opportunities to do the same aboard the scientific data-collecting ferry next summer. Thank you Kaitlyn Mullen and Frenchman Bay Research Boating for a great day on the water!

The Cammen Lab is seeking a graduate student interested in applying transcriptomic techniques to research questions related to marine mammal health. Example projects may include studying the cetacean stress response to noise exposure or immunogenomics of gray and harbor seals. In our lab we encourage students to explore interdisciplinary, collaborative research opportunities, including participation in lab work, field work, and bioinformatic training. Graduate students will have the opportunity to engage with colleagues in the School of Marine Sciences and Ecology & Environmental Sciences Program, as well as the new interdisciplinary Center for One Health and the Environment at the University of Maine.
Prospective students must hold a Bachelor’s degree in biology, ecology, evolution, genetics, bioinformatics, or a related field. Preferred candidates will have a Masters degree or equivalent experience, and prior experience with molecular analyses. Interested students with prior experience in non-model species genomics are highly encouraged to contact me.
Prospective students are strongly encouraged to apply for external funding, such as NSF graduate research fellowships, and I am happy to help support these funding applications, following initial conversations regarding your research interests and fit for our lab.
Interested qualified applicants are encouraged to email a cover letter and CV/resume to Kristina Cammen (kristina.cammen@maine.edu).
Kristina presented her findings on the impacts of historical bottleneck, recent recovery, and geographic expansion in gray and harbor seals* at the Gordon Research Conference (GRC) on Ecological and Evolutionary Genomics in Biddeford, Maine. GRC’s are scientific meetings with an explicit focus on cutting-edge research and promoting scientific discussion. This year’s meeting spanned the spectrum from model to non-model system, and from theoretical to empirical. It left me feeling inspired and excited to apply new sequencing technologies and analytical pipelines to marine mammal species in an effort to better understand their ecology and evolution.
*Stay tuned for new publications that summarize this work soon!